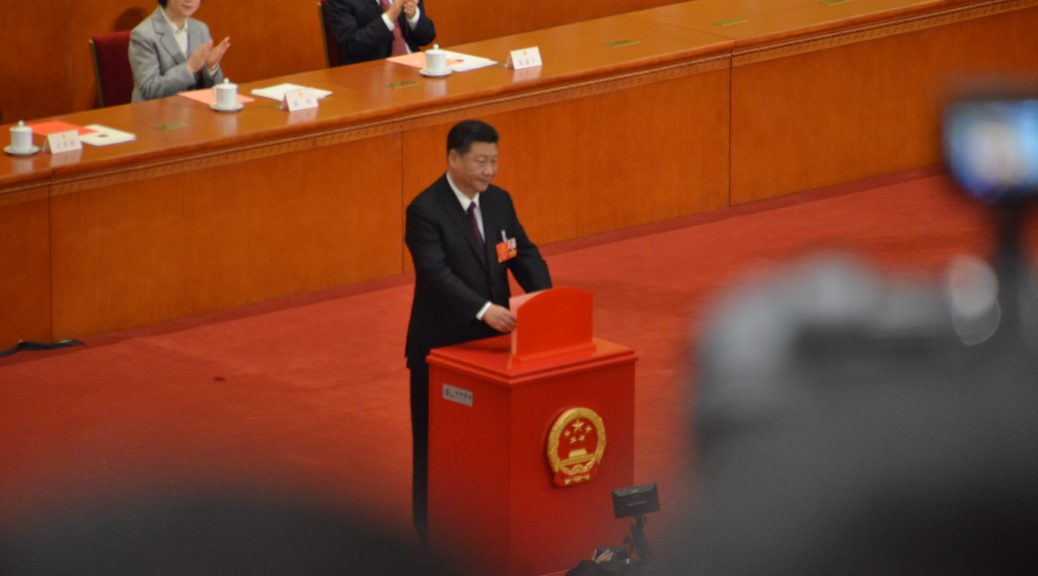
BEIJING — The State Council Information Office of the People’s Republic of China published a white paper titled “China’s Arctic Policy” on Jan 26.
Following is the full text of the white paper:
China’s Arctic Policy
The State Council Information Office of the People’s Republic of China
January 2018
First Edition 2018
Contents
Foreword
I. The Arctic Situation and Recent Changes
II. China and the Arctic
III. China’s Policy Goals and Basic Principles on the Arctic
IV. China’s Policies and Positions on Participating in Arctic Affairs
1. Deepening the exploration and understanding of the Arctic
2. Protecting the eco-environment of the Arctic and addressing climate change
3. Utilizing Arctic Resources in a Lawful and Rational Manner
4. Participating Actively in Arctic governance and international cooperation
5. Promoting peace and stability in the Arctic Conclusion
Conclusion
Foreword
Global warming in recent years has accelerated the melting of ice and snow in the Arctic region. As economic globalization and regional integration further develops and deepens, the Arctic is gaining global significance for its rising strategic, economic values and those relating to scientific research, environmental protection, sea passages, and natural resources. The Arctic situation now goes beyond its original inter-Arctic States or regional nature, having a vital bearing on the interests of States outside the region and the interests of the international community as a whole, as well as on the survival, the development, and the shared future for mankind. It is an issue with global implications and international impacts.
A champion for the development of a community with a shared future for mankind, China is an active participant, builder and contributor in Arctic affairs who has spared no efforts to contribute its wisdom to the development of the Arctic region. The Chinese government hereby issues this white paper, to expound its basic positions on Arctic affairs, to elaborate on its policy goals, basic principles and major policies and positions regarding its engagement in Arctic affairs, to guide relevant Chinese government departments and institutions in Arctic-related activities and cooperation, to encourage relevant parties to get better involved in Arctic governance, and to work with the international community to safeguard and promote peace and stability in, and the sustainable development of, the Arctic.
I. The Arctic Situation and Recent Changes
The Arctic is situated at a special geographical location. It commonly refers to the area of land and sea north of the Arctic Circle (approximately 66 degrees 34 minutes N), totaling about 21 million square kilometers. In the context of international law, the Arctic includes the northernmost landmasses of Europe, Asia and North America adjacent to the Arctic Ocean and the relevant islands, and a combination of sea areas within national jurisdiction, high seas, and the Area in the Arctic Ocean. There is no single comprehensive treaty for all Arctic affairs. The Charter of the United Nations, the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), the Spitsbergen Treaty and other treaties and general international law govern Arctic affairs at present.
The continental and insular land territories in the Arctic cover an area of about 8 million square kilometers, with sovereignty over them belonging to Canada, Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, Russia, Sweden and the United States, respectively. The Arctic Ocean covers an area of more than 12 million square kilometers, in which coastal States and other States share maritime rights and interests in accordance with international law. These coastal States have within their jurisdiction internal waters, territorial seas, contiguous zones, exclusive economic zones, and continental shelves in the Arctic Ocean. Certain areas of the Arctic Ocean form part of the high seas and the Area.
States from outside the Arctic region do not have territorial sovereignty in the Arctic, but they do have rights in respect of scientific research, navigation, overflight, fishing, laying of submarine cables and pipelines in the high seas and other relevant sea areas in the Arctic Ocean, and rights to resource exploration and exploitation in the Area, pursuant to treaties such as UNCLOS and general international law. In addition, Contracting Parties to the Spitsbergen Treaty enjoy the liberty of access and entry to certain areas of the Arctic, the right under conditions of equality and, in accordance with law, to the exercise and practice of scientific research, production and commercial activities such as hunting, fishing, and mining in these areas.
The Arctic boasts a unique natural environment and rich resources, with most of its sea area covered under thick ice for most of the year. The Arctic natural environment is now undergoing rapid changes. Over the past three decades, temperature has been rising continuously in the Arctic, resulting in diminishing sea ice in summer. Scientists predict that by the middle of this century or even earlier, there may be no ice in the Arctic Ocean for part of the year. On the one hand, melting ice in the Arctic has led to changes in the natural environment, or possibly can result in accelerated global warming, rising sea levels, increased extreme weather events, damaged biodiversity, and other global problems. On the other, with the ice melted, conditions for the development of the Arctic may be gradually changed, offering opportunities for the commercial use of sea routes and development of resources in the region. Commercial activities in the region will have considerable impact on global shipping, international trade and energy supply, bring about major social and economic changes, and exert important influence on the way of work and life of Arctic residents including the indigenous peoples. They may also pose a potential threat to the ecological environment of the Arctic. The international community faces the same threat and shares the same future in addressing global issues concerning the Arctic.
II. China and the Arctic
China is an important stakeholder in Arctic affairs. Geographically, China is a “Near-Arctic State”, one of the continental States that are closest to the Arctic Circle. The natural conditions of the Arctic and their changes have a direct impact on China’s climate system and ecological environment, and, in turn, on its economic interests in agriculture, forestry, fishery, marine industry and other sectors.
China is also closely involved in the trans-regional and global issues in the Arctic, especially in such areas as climate change, environment, scientific research, utilization of shipping routes, resource exploration and exploitation, security, and global governance. These issues are vital to the existence and development of all countries and humanity, and directly affect the interests of non-Arctic States including China. China enjoys the freedom or rights of scientific research, navigation, overflight, fishing, laying of submarine cables and pipelines, and resource exploration and exploitation in the high seas, the Area and other relevant sea areas, and certain special areas in the Arctic Ocean, as stipulated in treaties such as the UNCLOS and the Spitsbergen Treaty, and general international law. As a permanent member of the UN Security Council, China shoulders the important mission of jointly promoting peace and security in the Arctic. The utilization of sea routes and exploration and development of the resources in the Arctic may have a huge impact on the energy strategy and economic development of China, which is a major trading nation and energy consumer in the world. China’s capital, technology, market, knowledge and experience is expected to play a major role in expanding the network of shipping routes in the Arctic and facilitating the economic and social progress of the coastal States along the routes. China has shared interests with Arctic States and a shared future with the rest of the world in the Arctic.
China has long been involved in Arctic affairs. In 1925, China joined the Spitsbergen Treaty and started to participate in addressing the Arctic affairs. Since then, China has exerted more efforts in the exploration of the Arctic, expanding the scope of activities, gaining more experience and deepening cooperation with other participants. China’s membership in the International Arctic Science Committee in 1996 marked its more active participation in scientific research in the Arctic. Since 1999, China has organized a number of scientific expeditions in the Arctic, with its research vessel Xue Long (Snow Dragon) as the platform. In 2004, China built the Arctic Yellow River Station in Ny Alesund in the Spitsbergen Archipelago. By the end of 2017, China has carried out eight scientific expeditions in the Arctic Ocean, and conducted research for 14 years with the Yellow River Station as the base. Using its research vessel and stations as platforms, China has gradually established a multi-discipline observation system covering the sea, ice and snow, atmosphere, biological, and geological system of the Arctic. The year 2005 saw China as the first Asian country to host the Arctic Science Summit Week, a high-level conference on Arctic affairs. In 2013, China became an accredited observer to the Arctic Council. In recent years, Chinese companies have begun to explore the commercial opportunities associated with Arctic shipping routes. China’s activities in the Arctic have gone beyond mere scientific research, and expanded into diverse areas of Arctic affairs including the platforms of global governance, regional cooperation, and bilateral and multilateral affairs, and such disciplines as scientific research, ecological environment, climate change, economic development, and cultural exchanges. As an important member of the international community, China has played a constructive role in the formulation of Arctic-related international rules and the development of its governance system. The Silk Road Economic Belt and the 21st-century Maritime Silk Road (Belt and Road Initiative), an important cooperation initiative of China, will bring opportunities for parties concerned to jointly build a “Polar Silk Road”, and facilitate connectivity and sustainable economic and social development of the Arctic.
III. China’s Policy Goals and Basic Principles on the Arctic
China’s policy goals on the Arctic are: to understand, protect, develop and participate in the governance of the Arctic, so as to safeguard the common interests of all countries and the international community in the Arctic, and promote sustainable development of the Arctic.
To understand the Arctic, China will improve the capacity and capability in scientific research on the Arctic, pursue a deeper understanding and knowledge of the Arctic science, and explore the natural laws behind its changes and development, so as to create favorable conditions for mankind to better protect, develop, and govern the Arctic.
To protect the Arctic, China will actively respond to climate change in the Arctic, protect its unique natural environment and ecological system, promote its own climatic, environmental and ecological resilience, and respect its diverse social culture and the historical traditions of the indigenous peoples.
To develop the Arctic, China will improve the capacity and capability in using applied Arctic technology, strengthen technological innovation, environmental protection, resource utilization, and development of shipping routes in the Arctic, and contribute to the economic and social development of the Arctic, improve the living conditions of the local people and strive for common development.
To participate in the governance of the Arctic, China will participate in regulating and managing the affairs and activities relating to the Arctic on the basis of rules and mechanisms. Internationally, China is committed to the existing framework of international law including the UN Charter, UNCLOS, treaties on climate change and the environment, and relevant rules of the International Maritime Organization, and to addressing various traditional and non-traditional security threats through global, regional, multilateral and bilateral mechanisms, and to building and maintaining a just, reasonable and well-organized Arctic governance system. Domestically, China will regulate and manage Arctic-related affairs and activities within its jurisdiction in accordance with the law, steadily enhance its ability to understand, protect and develop the Arctic, and actively participate in international cooperation in Arctic affairs.
Through all the above efforts to understand, protect, develop and participate in the governance of the Arctic, China will work with all other countries to build a community with a shared future for mankind in the Arctic region. While pursuing its own interests, China will pay due regard to the interests of other countries and the broader international community, bear in mind the importance of the protection and development of the Arctic, and of keeping in proper balance its current and long-term interests, so as to promote the sustainable development of the Arctic.
In order to realize the above-mentioned policy goals, China will participate in Arctic affairs in accordance with the basic principles of “respect, cooperation, win-win result and sustainability”.
“Respect” is the key basis for China’s participation in Arctic affairs. Respect should be reciprocal. It means all States should abide by international treaties such as the UN Charter and the UNCLOS, as well as general international law. They should respect the sovereignty, sovereign rights, and jurisdiction enjoyed by the Arctic States in this region, respect the tradition and culture of the indigenous peoples, as well as respect the rights and freedom of non-Arctic States to carry out activities in this region in accordance with the law, and respect the overall interests of the international community in the Arctic.
“Cooperation” is an effective means for China’s participation in Arctic affairs. It means establishing a relationship of multi-level, omni-dimensional and wide-ranging cooperation in this area. Through global, regional, multilateral and bilateral channels, all stakeholders — including States from both inside and outside the Arctic, intergovernmental organizations, and nonstate entities — are encouraged to take part in cooperation on climate change, scientific research, environmental protection, shipping route development, resource utilization and cultural activities.
“Win-win result” is the value pursuit of China’s participation in Arctic affairs. It means all stakeholders in this area should pursue mutual benefit and common progress in all fields of activities. Such cooperation should ensure that the benefits are shared by both Arctic and non-Arctic States as well as by nonstate entities, and should accommodate the interests of local residents including the indigenous peoples. It should also help to promote coordinated development of activities in all fields to ensure the harmony between natural conservation and social development.
“Sustainability” is the fundamental goal of China’s participation in Arctic affairs. This means promoting the sustainable development of the Arctic by ensuring the sustainability of environmental protection, resource utilization and human activities in the area. It means realizing harmonious coexistence between man and nature, better coordination between ecological protection, economic growth and social progress, better balance between utilization, management and protection, and intergenerational equity.
IV. China’s Policies and Positions on Participating in Arctic Affairs
When participating in Arctic affairs, China prioritizes scientific research, underscores the importance of environmental protection, rational utilization, law-based governance and international cooperation, and commits itself to maintaining a peaceful, secure and stable Arctic order.
1. Deepening the exploration and understanding of the Arctic
The Arctic holds great value for scientific research. To explore and understand the Arctic serves as the priority and focus for China in its Arctic activities.
China actively promotes scientific expedition and research in the Arctic. China respects the Arctic States’ exclusive jurisdiction over research activities under their national jurisdiction, maintains that scientific research in areas under the jurisdiction of Arctic States should be carried out through cooperation in accordance with the law, and stresses that all States have the freedom of scientific research on the high seas of the Arctic Ocean. China is actively involved in multi-disciplinary research including Arctic geology, geography, ice and snow, hydrology, meteorology, sea ice, biology, ecology, geophysics and marine chemistry. It actively participates in monitoring and assessing local climatic and environmental changes, and carries out multi-level and multi-domain continuous observation of atmosphere, sea, sea ice, glaciers, soil, bio-ecological character and environmental quality through the establishment of multi-element Arctic observation system, construction of cooperative research (observation) stations, and development of and participation in the Arctic observation network. China is committed to improving its capacity in Arctic expedition and research, strengthening the construction, maintenance and functions of research stations, vessels and other supporting platforms in the Arctic, and promoting the building of icebreakers for scientific purposes.
China supports and encourages research activities in the Arctic by constantly increasing investment in scientific research, building modernized research platforms, and improving the capacity in, and level of, research on the Arctic. It is making a greater effort to advance research in the fields of natural science, climate change and ecological environment, accelerate the development of basic subjects such as physics, chemistry, life science and earth science, strengthen social science research including Arctic politics, economy, law, society, history, culture and management of Arctic activities, and promote innovation in both natural and social sciences. It is also working to strengthen personnel training and public awareness of the Arctic, support higher learning and research institutions to train professionals specialized in natural and social sciences on the Arctic, build science popularization and education centers, and publish cultural products on the Arctic to improve public knowledge. It actively promotes international cooperation on Arctic research, pushes for an open and inclusive international monitoring network of the Arctic environment, supports pragmatic cooperation through platforms such as the International Arctic Science Committee, encourages Chinese scientists to carry out international academic exchanges and cooperation on the Arctic, and encourages Chinese higher learning and research institutions to join the network of the University of the Arctic.
The availability of technical equipment is essential to understanding, utilizing and protecting the Arctic. China encourages the development of environment-friendly polar technical equipment, actively participates in the building of infrastructure for Arctic development, pushes for the upgrade of equipment in the fields of deep sea exploration, ice zone prospecting, and atmosphere and biology observation, and promotes technology innovation in Arctic oil and gas drilling and exploitation, renewable energy development, navigation and monitoring in ice zones, and construction of new-type icebreakers.
2. Protecting the eco-environment of the Arctic and addressing climate change
China follows international law in the protection of the natural environment and ecosystem of the Arctic and conservation of its biological resources, and takes an active part in addressing the challenges of environmental and climate change in the Arctic.
(1) Protecting the Environment
China always gives top priority to resolving global environmental issues, earnestly fulfills its obligations under relevant treaties, and discharges its responsibility of environmental protection. China is actively engaged in improving the Arctic environment by enhancing the environmental background investigation of Arctic activities and the assessment of their environmental impact. It respects the environmental protection laws and regulations of the Arctic States and calls for stronger environmental management and cooperation.
The marine environment is a key area for Arctic environmental protection. China supports the Arctic coastal States in their efforts to reduce pollutants in the Arctic waters from land-based sources, in accordance with the relevant treaties, and commits itself to raising the environmental responsibility awareness of its citizens and enterprises. In order to effectively protect the marine environment of the Arctic, China works with other States to enhance control of the sources of marine pollution such as ship discharge, offshore dumping, and air pollution.
(2) Protecting the Ecosystem
The Arctic is home to several endangered species of wild fauna and flora from around the globe. China attaches importance to the sustainable development and biodiversity protection of the Arctic. It conducts scientific evaluation of the impact on the Arctic ecological system caused by global climate change and human activities, strengthens protection of migratory birds and their habitats, organizes research on the migration patterns of Arctic migratory birds, improves the adaptability and resilience of the Arctic ecological system, and advances international cooperation in the protection of Arctic species of fauna and flora.
(3) Addressing climate change
Addressing climate change in the Arctic is an important part of global climate governance. China consistently takes the issue of climate change seriously. It has included measures to deal with climate change such as Nationally Determined Contributions in its overall national development agenda and planning, and has made significant contributions to the conclusion of the Paris Agreement. China’s emission reduction measures have a positive impact on the climatic and ecological environment of the Arctic. China is committed to studying the substance and energy exchange process and mechanisms of the Arctic, evaluating the interaction between the Arctic and global climate change, predicting potential risks posed by future climate change to the Arctic’s natural resources and ecological environment, and advancing Arctic cryospheric sciences. It strengthens publicity and education on addressing climate change to raise the public’s awareness of the issue, and promotes international cooperation in addressing climate change in the Arctic.
3. Utilizing Arctic Resources in a Lawful and Rational Manner
The Arctic has abundant resources, but a fragile ecosystem. China advocates protection and rational use of the region and encourages its enterprises to engage in international cooperation on the exploration for and utilization of Arctic resources by making the best use of their advantages in capital, technology and domestic market. China maintains that all activities to explore and utilize the Arctic should abide by treaties such as the UNCLOS and the Spitsbergen Treaty as well as general international law, respect the laws of the Arctic States, and proceed in a sustainable way on the condition of properly protecting the eco-environment of the Arctic and respecting the interests and concerns of the indigenous peoples in the region.
(1) China’s participation in the development of Arctic shipping routes
The Arctic shipping routes comprise the Northeast Passage, Northwest Passage, and the Central Passage. As a result of global warming, the Arctic shipping routes are likely to become important transport routes for international trade. China respects the legislative, enforcement and adjudicatory powers of the Arctic States in the waters subject to their jurisdiction. China maintains that the management of the Arctic shipping routes should be conducted in accordance with treaties including the UNCLOS and general international law and that the freedom of navigation enjoyed by all countries in accordance with the law and their rights to use the Arctic shipping routes should be ensured. China maintains that disputes over the Arctic shipping routes should be properly settled in accordance with international law.
China hopes to work with all parties to build a “Polar Silk Road” through developing the Arctic shipping routes. It encourages its enterprises to participate in the infrastructure construction for these routes and conduct commercial trial voyages in accordance with the law to pave the way for their commercial and regularized operation. China attaches great importance to navigation security in the Arctic shipping routes. It has actively conducted studies on these routes and continuously strengthened hydrographic surveys with the aim to improving the navigation, security and logistical capacities in the Arctic. China abides by the International Code for Ships Operating in Polar Waters (Polar Code), and supports the International Maritime Organization in playing an active role in formulating navigational rules for the Arctic. China calls for stronger international cooperation on infrastructure construction and operation of the Arctic routes.
(2) Participating in the exploration for and exploitation of oil, gas, mineral and other non-living resources
China respects the sovereign rights of Arctic States over oil, gas and mineral resources in the areas subject to their jurisdiction in accordance with international law, and respects the interests and concerns of residents in the region. It requires its enterprises to observe the laws of the relevant States and conduct risk assessments for resource exploration, and encourages them to participate in the exploitation of oil, gas and mineral resources in the Arctic, through cooperation in various forms and on the condition of properly protecting the eco-environment of the Arctic.
The Arctic region boasts an abundance of geothermal, wind, and other clean energy resources. China will work with the Arctic States to strengthen clean energy cooperation, increase exchanges in respect of technology, personnel and experience in this field, explore the supply of clean energy and energy substitution, and pursue low-carbon development.
(3) Participating in conservation and utilization of fisheries and other living resources
As fish stocks have shown a tendency to move northwards due to climate change and other factors, the Arctic has the potential to become a new fishing ground in the future. As regards fishing in the high seas in the Arctic Ocean, China has consistently held a firm stance in favor of conservation in a scientific manner and of rational use, and maintains that, while enjoying their lawful right to conduct fisheries research and development in the high seas in the Arctic Ocean, all States should fulfill their obligations to conserve the fishery resources and the ecosystem in the region.
China supports efforts to formulate a legally binding international agreement on the management of fisheries in the high seas portion of the Arctic Ocean. China also supports the establishment of an Arctic fisheries management organization or making other institutional arrangements based on the UNCLOS. China will strengthen survey on and research into the fishery resources in the high seas in the Arctic, carry out appropriate exploratory fishing, and play a constructive part in the management of fisheries in the high seas in the Arctic Ocean. China hopes to strengthen cooperation with the Arctic coastal States on the research, conservation, and utilization of fishery resources. China is committed to properly protecting Arctic biodiversity and advocates transparent and reasonable exploration and utilization of Arctic genetic resources, and fair and equitable sharing and use of the benefits generated by the exploitation of such resources.
(4) Participating in developing tourism resources
Arctic tourism is an emerging industry, and China is a source of tourists to the Arctic. China supports and encourages its enterprises to cooperate with Arctic States in developing tourism in the region, and calls for continuous efforts to enhance security, insurance, and rescue systems to ensure the safety of tourists in the Arctic. China conducts training for and regulates Chinese tourism agencies and professionals involved in Arctic tourism, and endeavors to raise the environmental awareness of Chinese tourists. China advocates low-carbon tourism, ecotourism, and responsible tourism, and hopes to contribute to the sustainable development of Arctic tourism.
China takes part in the development and utilization of Arctic resources on the condition of respecting the traditions and cultures of the Arctic residents including the indigenous peoples, preserving their unique lifestyles and values, and respecting the efforts made by the Arctic States to empower the local citizens, foster their social and economic progress, and improve education and medical services, so that the Arctic residents, including the indigenous peoples, will truly benefit from the development of Arctic resources.
4. Participating Actively in Arctic governance and international cooperation
China is committed to improving and complementing the Arctic governance regime. China has worked to regulate and supervise the activities of Chinese citizens, legal persons or other organizations in the Arctic in accordance with the law to ensure that their activities accord with international law and respect the relevant national laws on environmental protection, resource conservation, and sustainable development. And it has endeavored to strengthen overall coordination of its Arctic policy and related affairs. Furthermore, China takes an active part in the international governance of the Arctic. China upholds the current Arctic governance system with the UN Charter and the UNCLOS as its core, plays a constructive part in the making, interpretation, application and development of international rules regarding the Arctic, and safeguards the common interests of all nations and the international community.
China stands for steadily advancing international cooperation on the Arctic. It has worked to strengthen such cooperation under the Belt and Road Initiative according to the principle of extensive consultation, joint contribution and shared benefits and emphasized policy coordination, infrastructure connectivity, unimpeded trade, financial integration, and closer people-to-people ties. Concrete cooperation steps include coordinating development strategies with the Arctic States, encouraging joint efforts to build a blue economic passage linking China and Europe via the Arctic Ocean, enhancing Arctic digital connectivity, and building a global infrastructure network. China hopes to work for the common good of all parties and further common interests through the Arctic.
At the global level, China actively participates in the formulation of rules concerning the global environment, climate change, international maritime issues, and high seas fisheries management, and fulfills all its international obligations in accordance with the law. China expands cooperation with various States and international organizations in environmental protection, and promotes energy conservation, emissions reduction, and low-carbon development. China also promotes global cooperation in tackling climate change, and upholds the principles of equity, common but differentiated responsibilities, and respective capabilities. It urges developed countries to fulfill their commitments under the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change, the Kyoto Protocol, and the Paris Agreement, and provides support to fellow developing countries in addressing climate change. China plays a constructive role in the work of the International Maritime Organization, and makes solid efforts to fulfill its international responsibilities for ensuring maritime navigational security and preventing its ships from polluting the maritime environment. China advocates stronger international cooperation in maritime technology and a globally coordinated solution to reducing greenhouse gas emissions from maritime transport under the International Maritime Organization framework. China takes an active part in negotiations over high seas fisheries regulation in the Arctic, and calls for a legally binding international agreement for managing fishery resources in the high seas portion of the Arctic. The agreement should allow scientific research and exploratory fishing activities in the high seas portion of the Arctic, and protect the freedom of all States on the high seas in accordance with international law.
At the regional level, China takes an active part in Arctic intergovernmental mechanisms. China, as an accredited observer to the Arctic Council, highly values the Council’s positive role in Arctic affairs, and recognizes it as the main intergovernmental forum on issues regarding the environment and sustainable development of the Arctic. China stands by the commitments it made when applying to become an observer to the Council. It fully supports the work of the Council, and dispatches experts to participate in the work of the Council including its Working Groups and Task Forces. China respects the Agreement on Cooperation on Aeronautical and Maritime Search and Rescue in the Arctic, the Agreement on Cooperation on Marine Oil Pollution Preparedness and Response in the Arctic, and the Agreement on Enhancing International Arctic Scientific Cooperation, all adopted by the Arctic Council. China also supports international cooperation through such platforms as the Arctic Science Ministerial Meeting.
At the bilateral and multilateral levels, China promotes practical cooperation in all fields, especially regarding climate change, scientific expeditions, environmental protection, ecosystems, shipping routes, resource development, submarine fiber-optic cables, cultural exchanges, and capacity building. China proposes to form cooperative partnerships between Arctic and non-Arctic States, and has carried out bilateral consultations on Arctic affairs with all Arctic States. In 2010, China and the United States set up an annual dialogue mechanism for bilateral dialogues on the law of the sea and polar issues. Since 2013, China and Russia have been conducting dialogues on Arctic issues. In 2012, China and Iceland signed the Framework Agreement on Arctic Cooperation, which was the first intergovernmental agreement on Arctic issues between China and an Arctic State. China also values cooperation with other non-Arctic States. It has conducted bilateral dialogues on the law of the sea and polar issues with the United Kingdom and France. In 2016, China, Japan and the Republic of Korea launched high-level trilateral dialogues on Arctic issues to promote exchanges on policies, practices, and experience regarding Arctic international cooperation, scientific research, and commercial cooperation.
China supports the participation of all Arctic stakeholders in Arctic governance and international cooperation. China supports platforms such as “The Arctic: Territory of Dialogue”, “The Arctic Circle”, “Arctic Frontiers”, “The China-Nordic Arctic Research Center”, in promoting exchanges and cooperation among the stakeholders. China also supports the participation of research institutions and enterprises in Arctic governance with their own expertise put to good use. China encourages research institutions to communicate with foreign think tanks and academic institutions, and supports enterprises to participate in the commercial development and utilization of the Arctic in a lawful and orderly manner.
5. Promoting peace and stability in the Arctic
Peace and stability in the Arctic provides a significant guarantee for all activities in the region, and serves the fundamental interest of all countries including China. China calls for the peaceful utilization of the Arctic and commits itself to maintaining peace and stability, protecting lives and property, and ensuring the security of maritime trade, operations and transport in the region. China supports the peaceful settlement of disputes over territory and maritime rights and interests by all parties concerned in accordance with such treaties as the UN Charter and the UNCLOS and general international law, and supports efforts to safeguard security and stability in the region. China strives to reinforce cooperation with the Arctic States in maritime and air search and rescue, maritime early warning, emergency response, and information sharing in order to properly handle security challenges such as maritime accidents, environmental pollution, and maritime crimes.
Conclusion
The future of the Arctic concerns the interests of the Arctic States, the wellbeing of non-Arctic States and that of the humanity as a whole. The governance of the Arctic requires the participation and contribution of all stakeholders. On the basis of the principles of “respect, cooperation, win-win result and sustainability”, China, as a responsible major country, is ready to cooperate with all relevant parties to seize the historic opportunity in the development of the Arctic, to address the challenges brought by the changes in the region, jointly understand, protect, develop and participate in the governance of the Arctic, and advance Arctic-related cooperation under the Belt and Road Initiative, so as to build a community with a shared future for mankind and contribute to peace, stability and sustainable development in the Arctic.
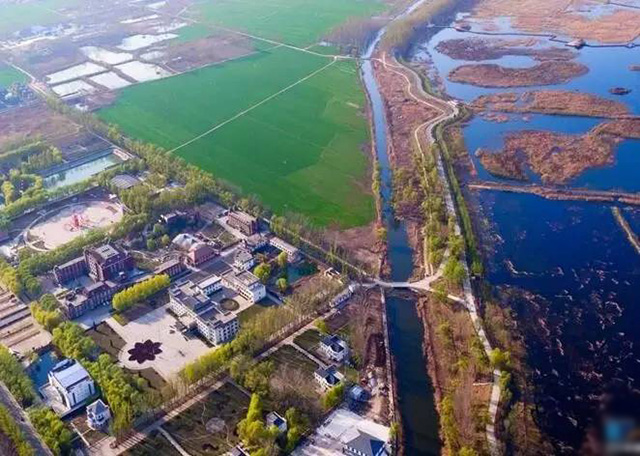


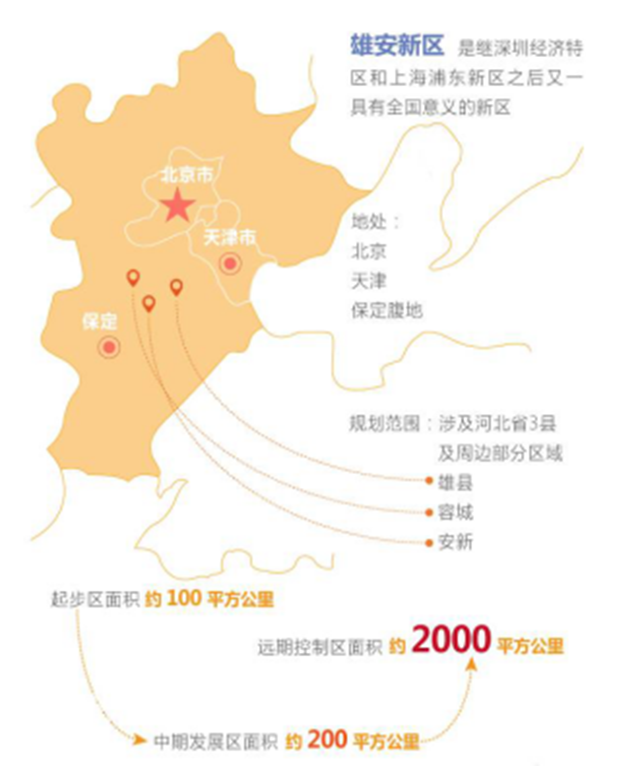
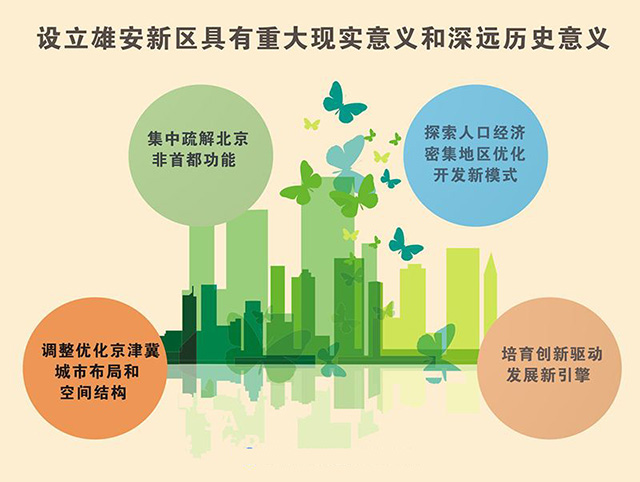



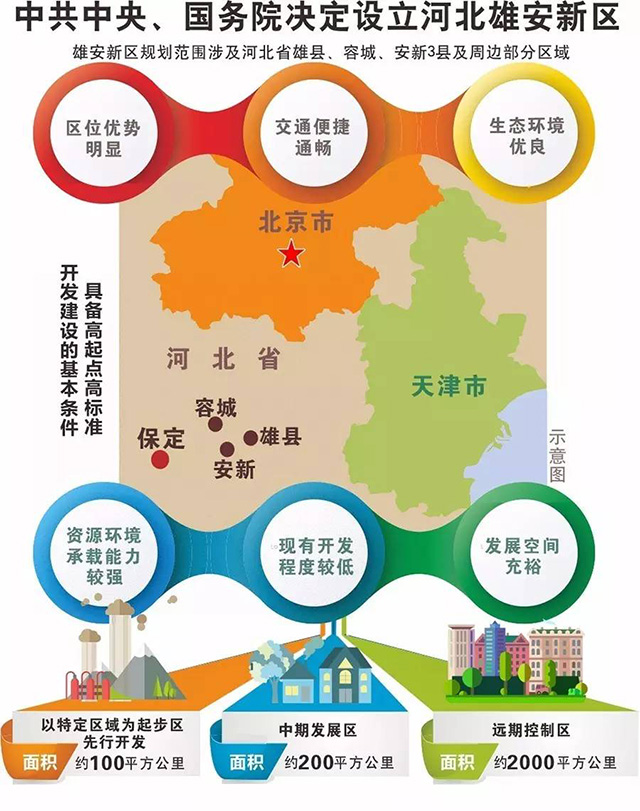

 雄安新区全景图
雄安新区全景图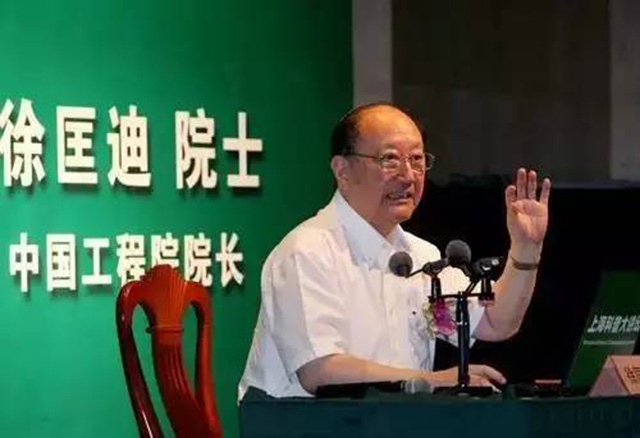 图为京津冀协同发展专家咨询委员会组长 徐匡迪
图为京津冀协同发展专家咨询委员会组长 徐匡迪










 更多精彩内容欢迎搜索关注微信公众号:原子智库(AtomThinkTank)
更多精彩内容欢迎搜索关注微信公众号:原子智库(AtomThinkTank)






















































